Many researchers analyze the impact of radio interference on GNSS signal reception:
Impact Study of Unintentional Interference on GNSS Receivers
GNSS Interference: Effects and Solutions
EFFECTS OF RADIO FREQUENCY INTERFERENCE ON GNSS RECEIVER OUTPUT
Albeit, some of our clients doubt that GNSS receivers can be susceptible to out-of-band radio interference.
This article demonstrates the practical results of GNSS receiver performance degradation due to the second harmonic of the DVB-T2 transmitter.
Customer Challenge
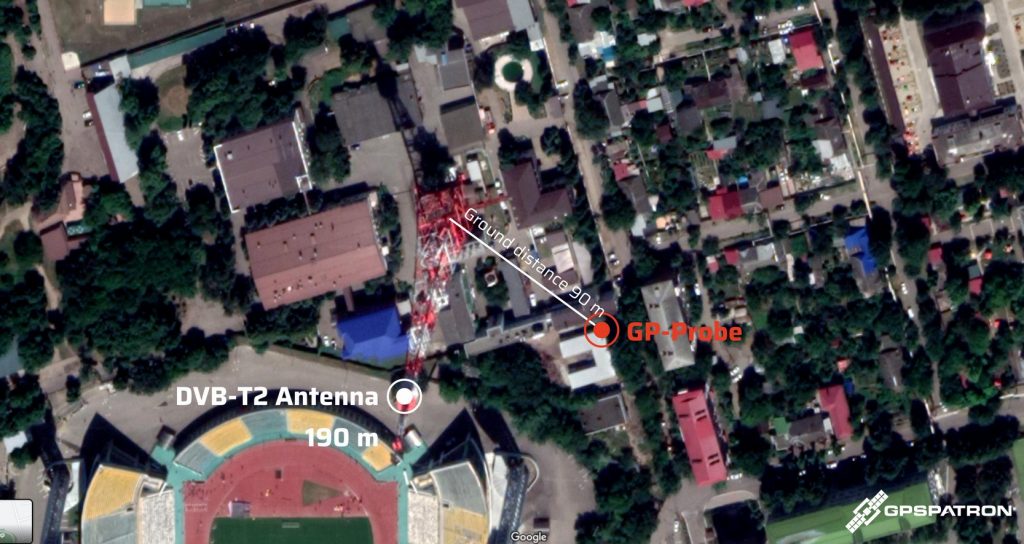
Our customer complains of poor quality GNSS reception near the TV tower. Our task is to make long-term GNSS signal measurements at different points and find the GNSS antenna’s best position.
DVB-T2 Transmitter Parameters
| Central Frequency | 768 MHz |
| Bandwidth | 8 MHz |
| Power, RMS | 5 kW |
| Modulation | 64QAM R5/6 |
| Second harmonic level | – 71 dB |
| Antenna height | 190 m |
| Antenna gain | 5 dB |
| Antenna radiation pattern | omnidirectional |



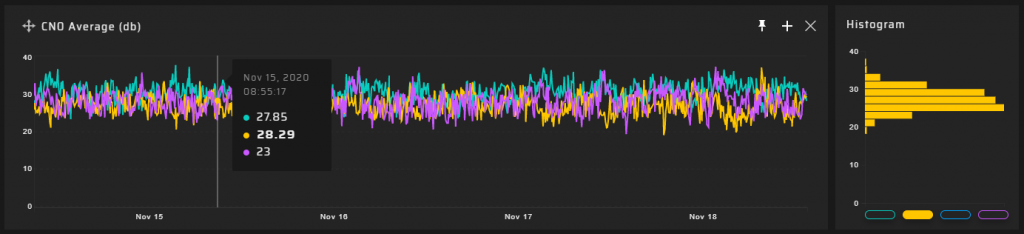
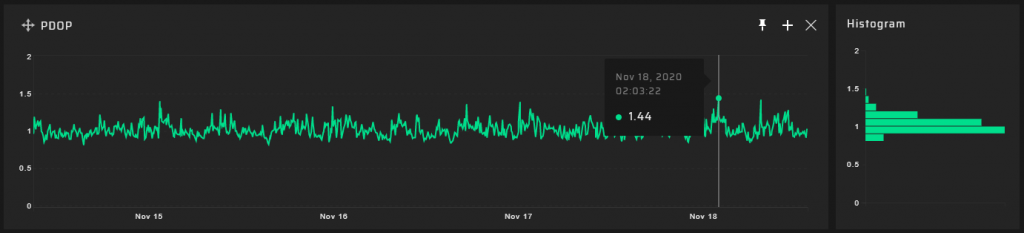
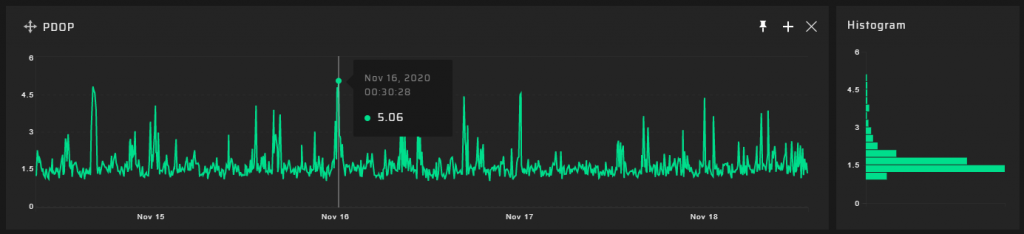
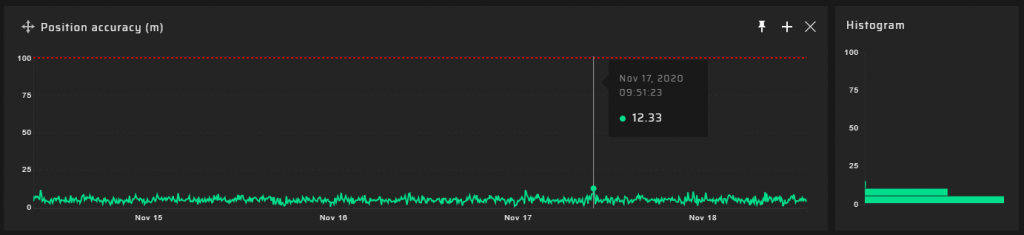
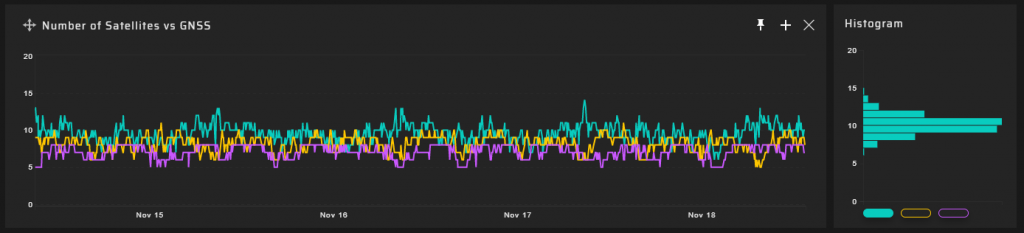
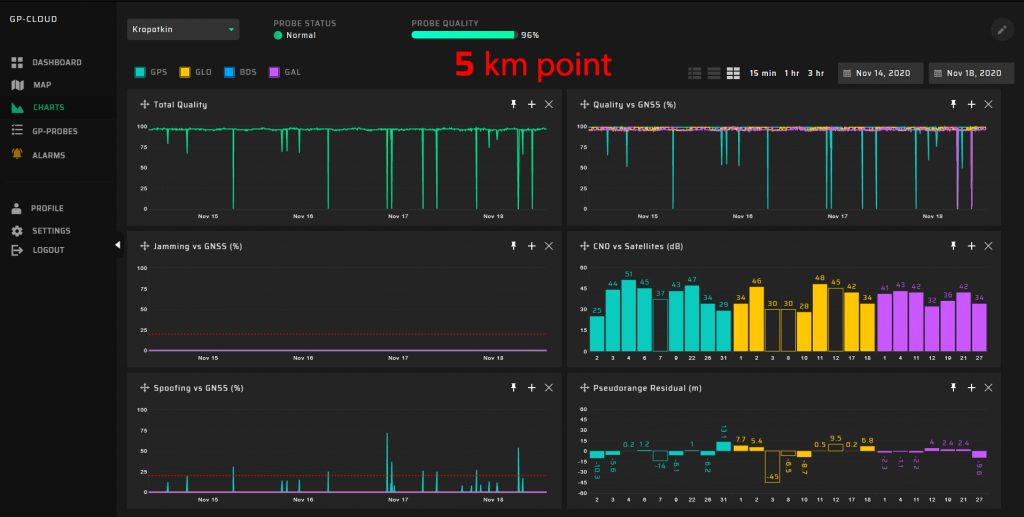
Measurement Results
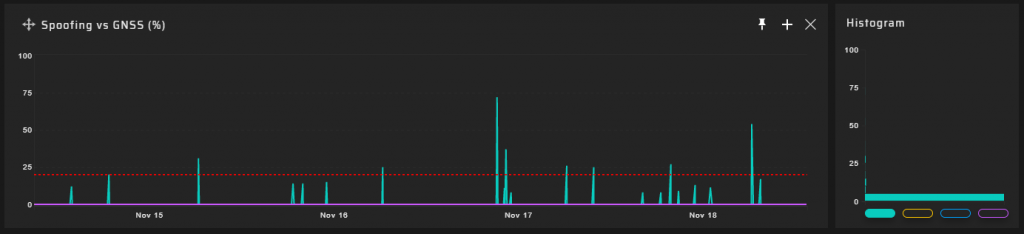
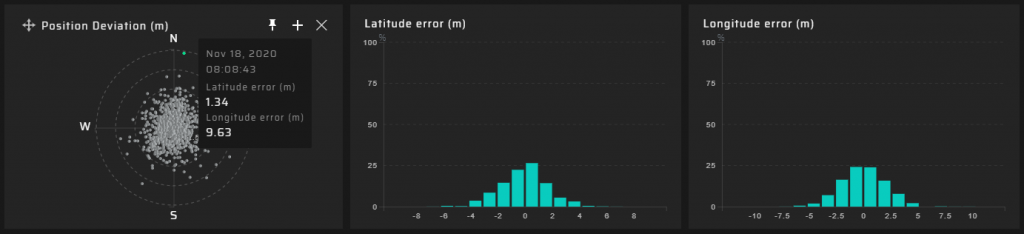
5 km Measuring Point
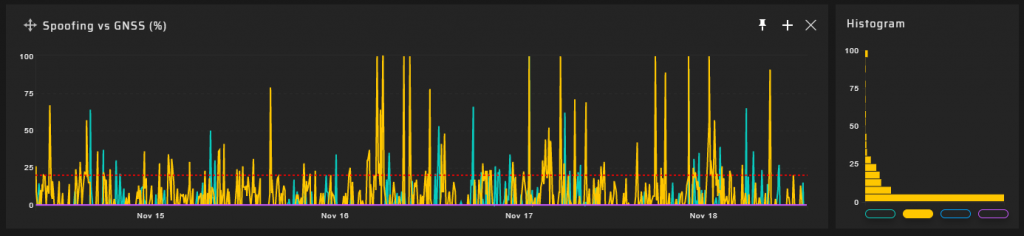
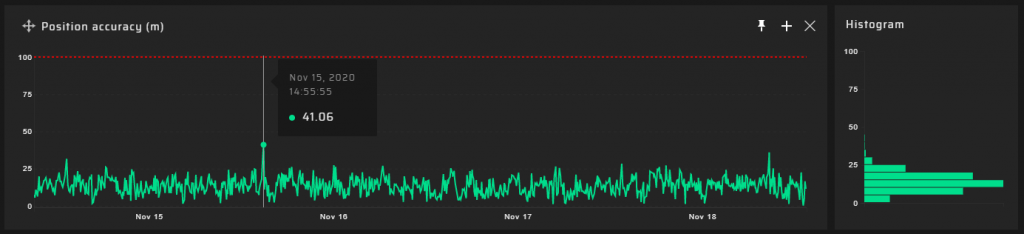
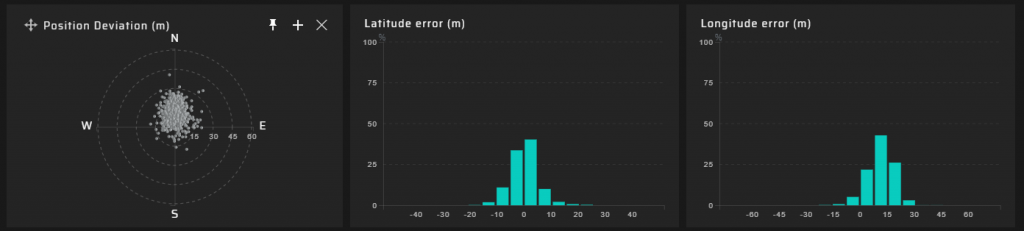
90 m Measuring Point
Conclusions
Hundreds of meters from the DVB-T2 transmitter @ 768 MHz, a significant degradation of the quality of the GNSS signal reception transpired. GNSS positioning accuracy decreases by a factor of five.
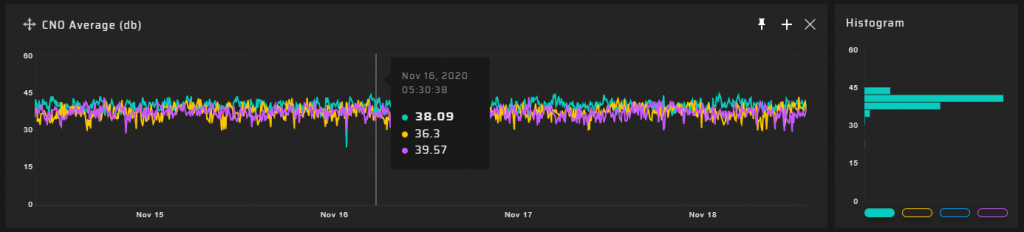
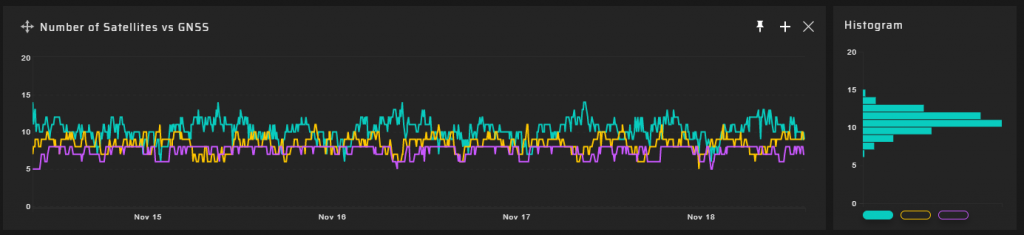
The number of visible satellites has a weak correlation with the interference level.