Nowadays, it is tough to find an industry not connected with satellite navigation whether directly or incidentally. GNSS is used extensively in critical applications requiring accurate time and position. In general, GNSS is utilized in two core areas:
Clock and Synchronization
- Exchanges and banks, for high-frequency trading in particular
- DVB-T/T2 in Single Frequency Networks mode
- Power monitoring and balancing systems
- Oil and gas pipelines (for measuring transferred volumes)
- 5G networks requiring high PPS phaseaccuracy
- Data Centers that require sub-millisecond precision timestamping
Positioning and Navigation
- Radio-technical flight support
- Transportation of dangerous goods
- Automatic train control
- Geodesy and mapmaking
Many factors can influence the accuracy and quality of GNSS operation:
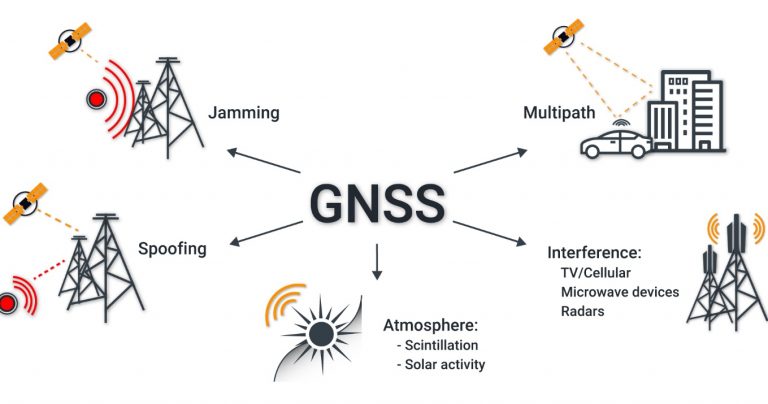

The quality of GNSS signals is affected by signal reflections from various objects, RF interferences from communication systems, terrestrial TV, etc. In densely populated cities many systems require accurate synchronization, but often it is not possible to mount a GNSS antenna high above buildings, trees, billboards, construction cranes. This adversely affects the accuracy of determining time, which is critical for some applications like 5G. If the antenna is unfittingly positioned, the accuracy of the PPS signal can drop to 500 ns.
The power of GNSS signals is as low as minus 155 dBW. Therefore, the receivers are ultra-sensitive to even out-of-band RF interferences generated by assorted electronic devices.
Since GNSS can play a key role in assuring numerous systems’ operability, it is essential to provide analysis and storage of navigation signal parameters for quick response to emergency events and the investigation. For example, if your network of GNSS RTK sites fails every so often, or you have many random errors during self-driven car tests, a tool should monitor the status of the navigation field.
GPSPATRON for Monitoring GNSS Signals
To start monitoring GNSS signals with GPSPATRON, mount the GP-Probe in control points and connect it to the GP-Cloud.
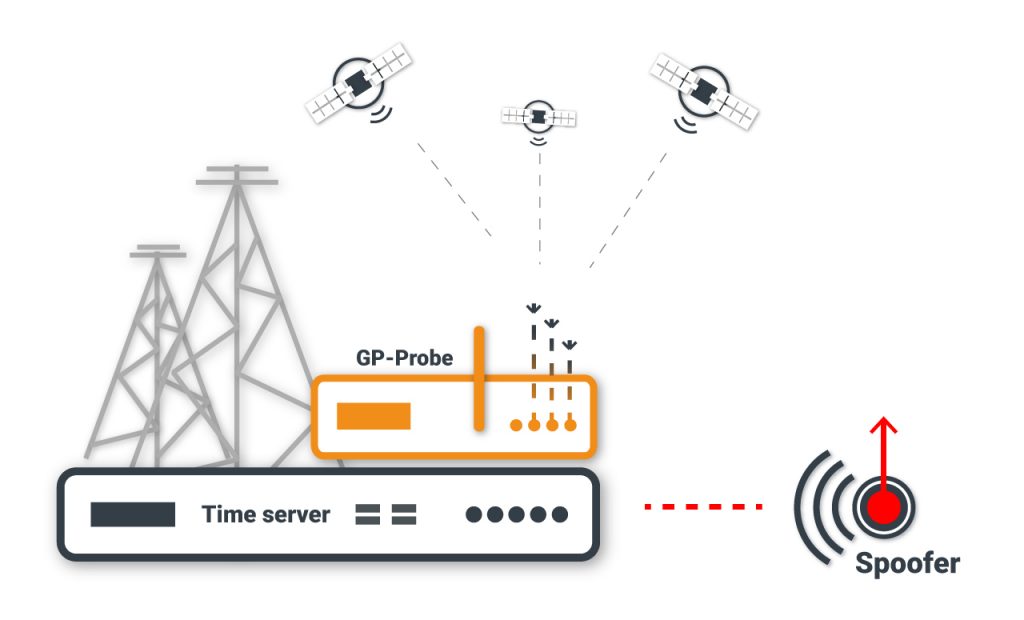
The GP-Cloud processes real-time data from GP-Probe, estimates the accuracy of time and position for all GNSSs, saves all signal parameters (SNR, pseudo-range, residual, phase, etc.) of each satellite to the database. If the parameters go beyond the set limits you will receive relevant notifications in real time. In case of failures of several elements of critical infrastructure, you will have the capability to analyze all stored data.
The GP-Cloud provides users with many tools for analyzing current and historical data:
- dashboard with statistics for last day/week/month or user-defined period
- map for real-time analysis
- charts for in-depth data analysis
- list of registered alarms
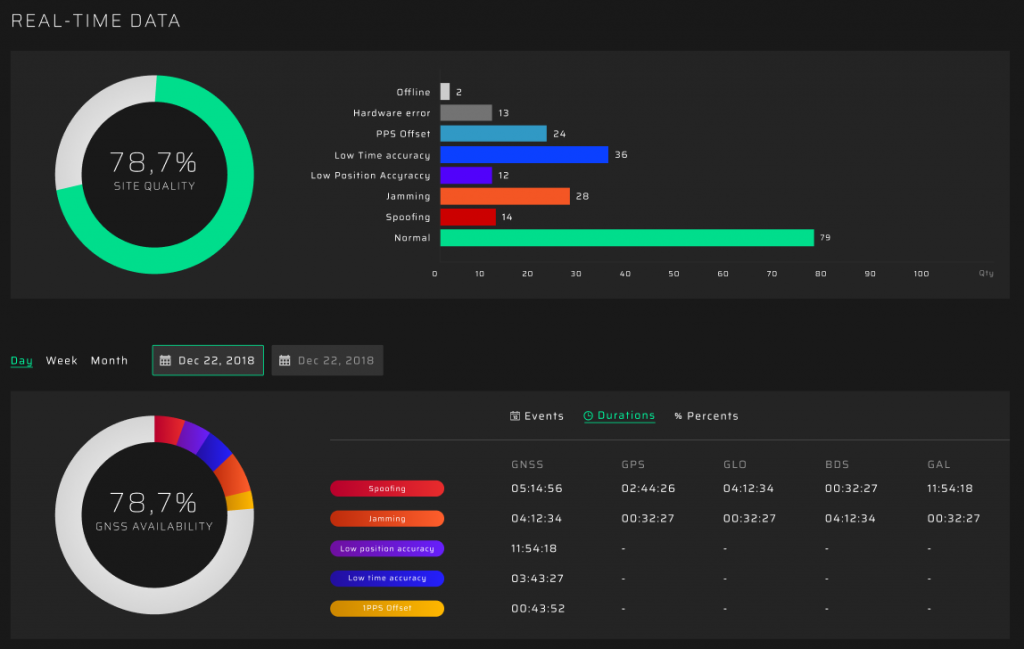
Dashboard
Information on the dashboard is displayed in two blocks:
- current status of GP-Probes in real time
- events analysis
The first block contains data about the entire site quality and GP-Probe status. Total site quality is calculated using the current values of the monitored parameters and set limits. The second block displays information about the quantity and duration of registered events in a defined period. All dashboard statistics are updated in real time.
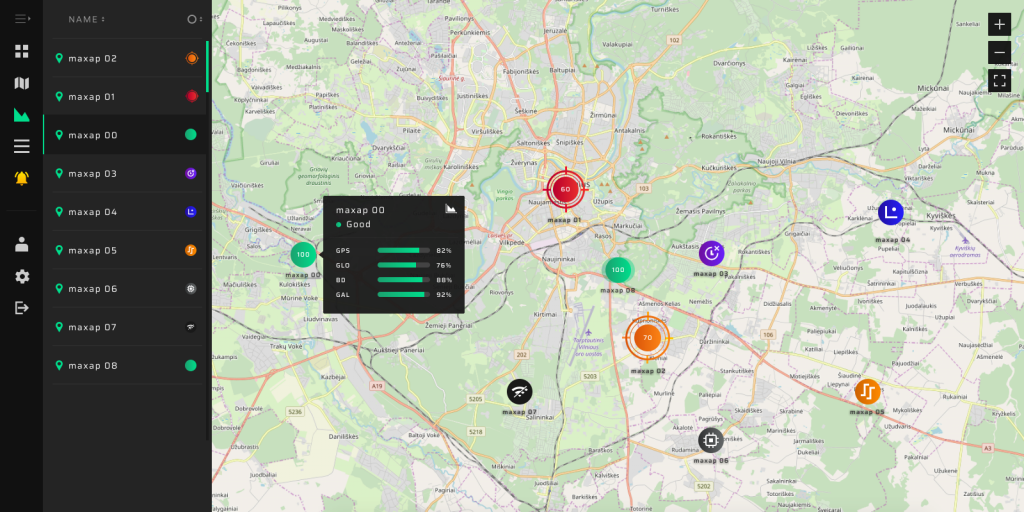
Map
You can see the GNSS signal status of all control points on the map. The status of each GP-Probe is indicated by assorted icons. Click on any icon to get detailed status information and open charts to analyze all the parameters.
List of GP-Probes statuses:
- Normal
- Spoofing
- Jamming
- PPS offset
- Low Position Accuracy
- LowTimeAccuracy
- Offline
- Hardware Error
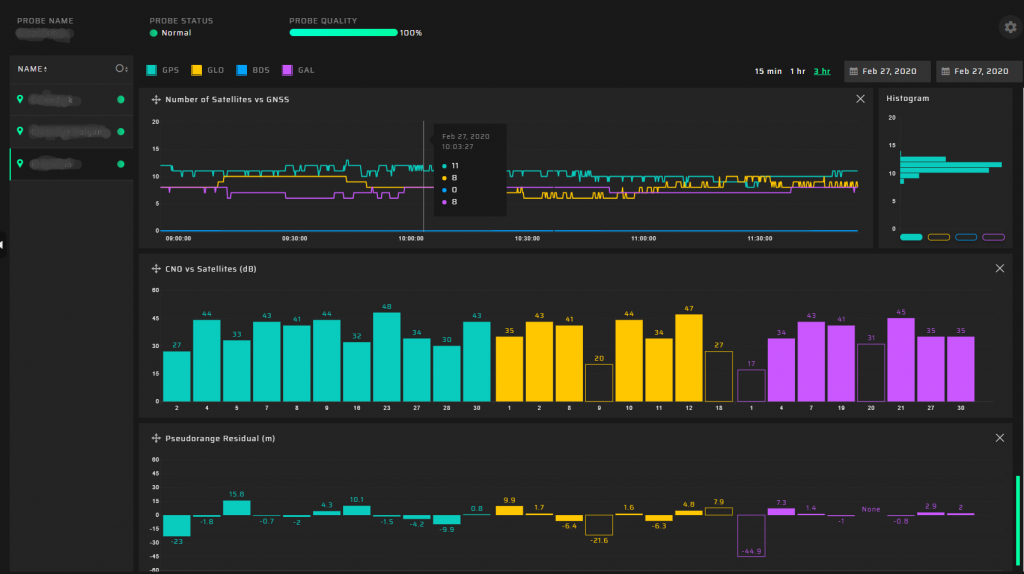
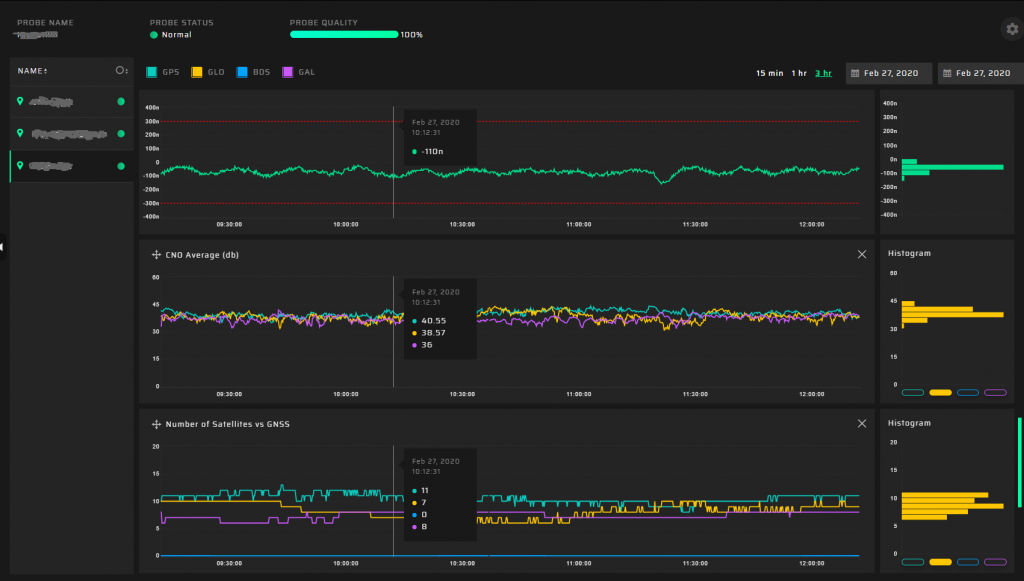
Charts
We are impressed with our charts’ design and believe our user interface is ideal for an in-depth analysis of complex parameters. Our charts have several features:
- all charts are coordinated to the selected scale
- cursors are synchronized on all charts
- three layouts
- real-timedataupdate
- scalingusingthemouse
Available charts:
- Total Quality
- Quality vs GNSS
- Spoofing vs GNSS
- Spoofing Investigation
- Position
- Satellite Heat Map
- Jamming vs GNSS
- Position Accuracy vs GNSS
- Time Accuracy vs GNSS
- Position Accuracy
- Time Accuracy
- PPS Offset
- CNO Average
- CNO vs Satellites
- Number of Satellites
- PDOP
- TDOP
- Pseudorange Residual
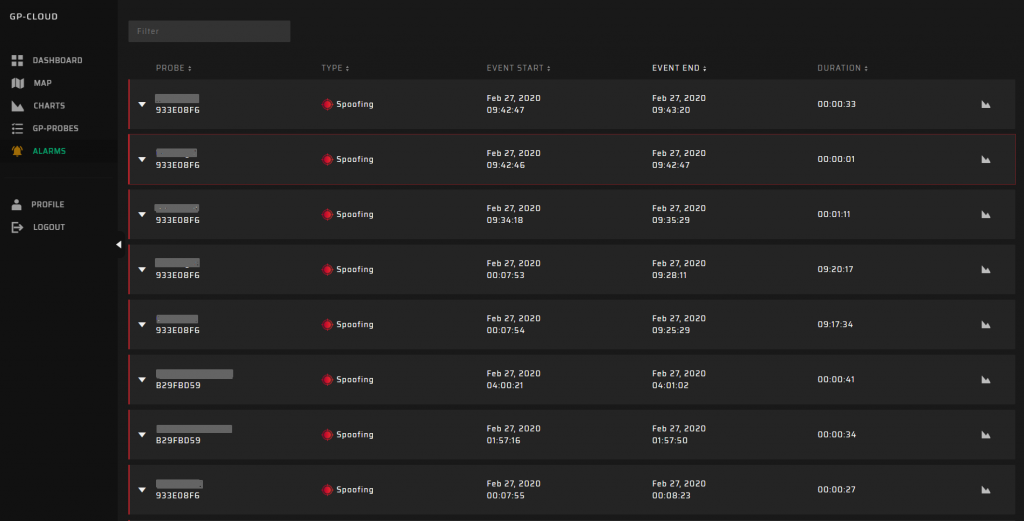
Alarms
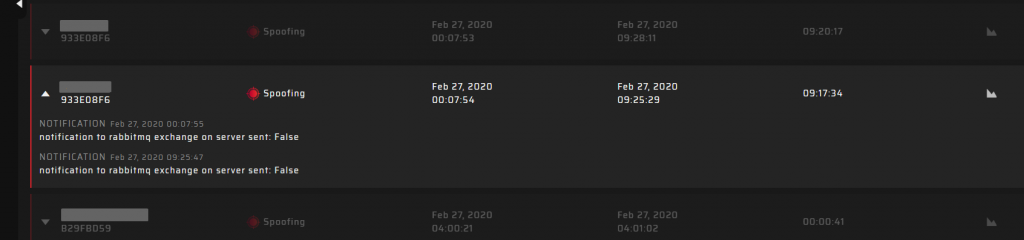
If set thresholds are surpassed, the GP-Cloud registers an accident. You can view the tabled list of accidents with exhaustive information about the type, start/end time, and duration. You can also click the chart icon to open diagrams for a detailed analysis.
The GP-Cloud sends user notifications when registering each accident according to system configuration. All performed actions are available for evaluation: